Ionic Mineral Technology (IMT) Facts
- Very small. ~ 1/30 size of metal Nano particles
- Positively charged - Cu++ strong attraction
- There are a lot of them - 1023 per liter of product
- 1.67x1017 per liter when diluted to 0.1 ppm
- 10,000 Copper ions end to end are roughly the length of a typical bacterial cell
- They are positively charged
- Many antimicrobial applications for algae, bacteria, fungi, and viruses
Ionic Copper Uses Multiple Modes of Action to Cause Cell Degeneration
- Our unique formulation allows the selective entry of biocidal copper into the cells of pathogenic bacteria and fungi through the peptidoglycan cell walls of bacteria and polysaccharide cell walls of fungi without direct entry into plant cell walls composed of cellulose and pectin.
- Positive charge on copper ions attracted to cell walls form electrostatic bonds with negative charged areas in cell.
- Electrostatic bonds create stresses in cell walls that distort cellular permeability and disrupt nutrient uptake that provide life to the cells.
- Once inside the cell the ions react with sulfur bearing amino acids in the protein structures.
- Cellular lyses (degeneration) occurs killing algae and fungi.
- Selective killing of undesirable bacteria occurs.
- Beneficial bacteria are tolerant to ionic copper.
Molecular Size of Copper Ion Increases Ability to Penetrate Bacterial Cell Membrane

The area of a copper ion measures 0.144 nanometers. The area of a copper ion is about 10-8 times smaller than that of a bacterial cell. To put this into perspective, if a bacterial cell were the size of a baseball stadium, a copper ion would be about the size of a US quarter.
Ionic Copper Uses Multiple Modes of Action To Cause Cell Degeneration
- Our unique formulation allows the selective entry of biocidal copper into the cells of pathogenic bacteria and fungi through the peptidoglycan cell walls of bacteria and polysaccharide cell walls of fungi without direct entry into plant cell walls composed of cellulose and pectin.
- Positive charge on copper ions attracted to cell walls form electrostatic bonds with negative charged areas in cell.
- Electrostatic bonds create stresses in cell walls that distort cellular permeability and disrupt nutrient uptake that provide life to the cells.
- Once inside the cell the ions react with sulfur bearing amino acids in the protein structures.
- Cellular lyses (degeneration) occurs killing algae and fungi.
- Selective killing of undesirable bacteria occurs.
- Beneficial bacteria are tolerant to ionic copper.
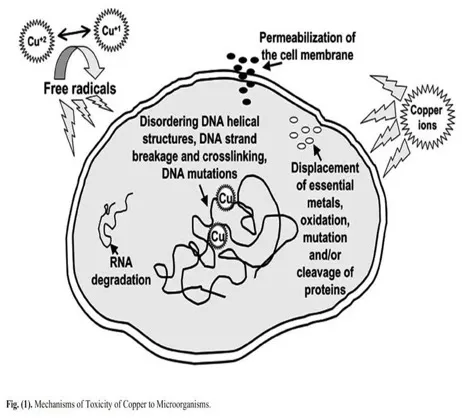
The result is the demise of algae, fungi and undesirable bacteria.
Further Superior Characteristics of Ionic Mineral Technology
Our unique IMT formulation process allows copper sulfate pentahydrate to remain in a fully dissolved state unlike other granular or suspended concentrate formulations that settle without agitation or dissolved liquid formulations that use chelation or sequestering agents to remain fully dissolved which reduces overall efficacy and the range of species controlled. The IMT process yields biologically active copper ions (Cu++) that remain in solution unencumbered by any agent or bond, disburse equally throughout the water column or tank mix and are available to attack their targets in proportion to biological demand indefinitely.

